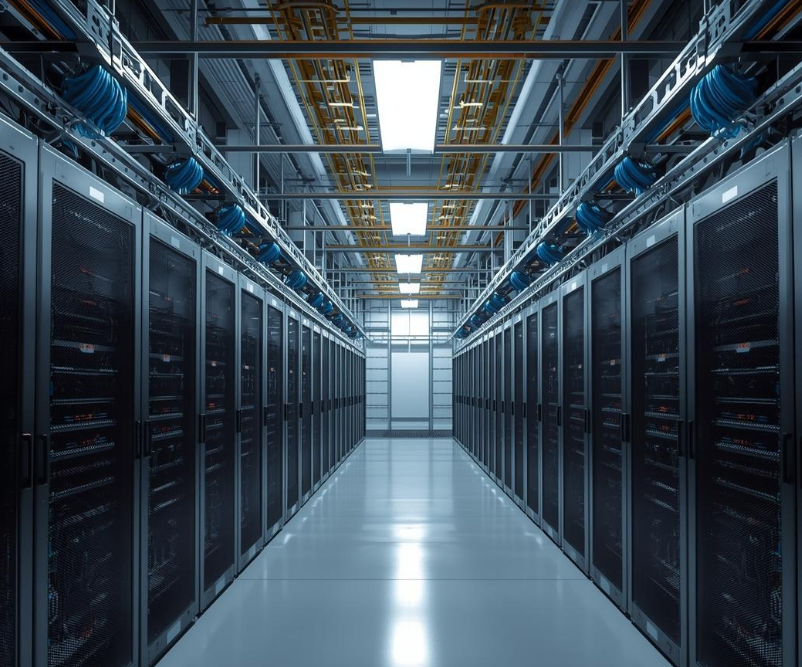

Gruber Communications Ladder Rack
Efficient cable management is essential in today’s data centers, telecom rooms, and
Learn More →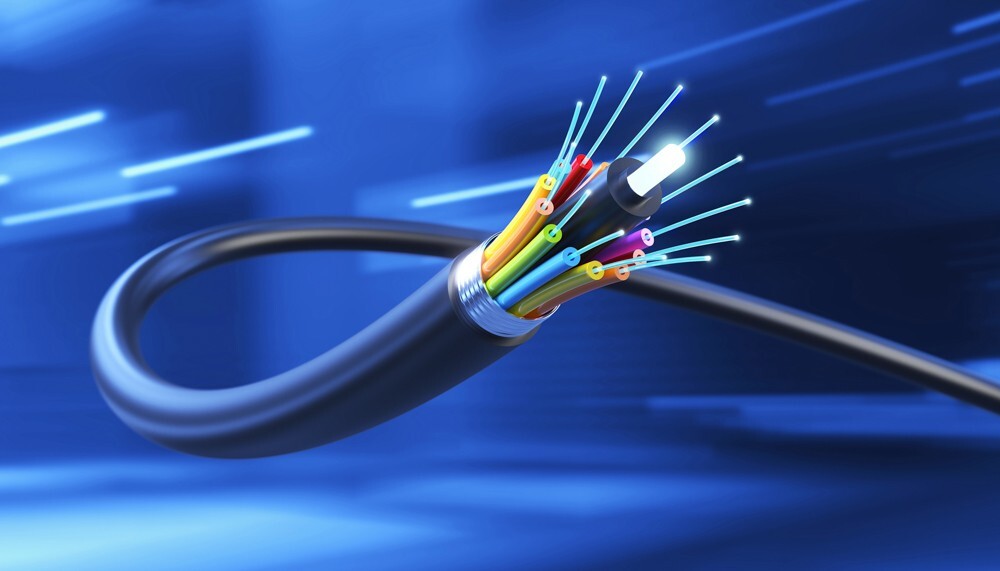
As the demand for faster and more reliable internet continues to grow, fiber optic cables have emerged as a cornerstone technology in modern data communication systems. This post explores the intricacies of fiber optic technology and its pivotal role in advancing connectivity across industries.
Fiber optic cables are composed of one or more thin strands of glass or plastic, known as optical fibers, which are capable of transmitting light signals over long distances with minimal loss. These cables are typically encased in a protective jacket to prevent physical damage and loss of signal. There are primarily two types of fiber optic cables:
Fiber optics offer several advantages over traditional copper cables:
These benefits make fiber optic cables ideal for modern communications, providing the infrastructure needed for ultra-fast internet services and robust data networks.
Fiber optic technology is versatile, finding applications across various sectors:
For instance, a financial institution might use fiber optic connections between its branches to ensure fast and secure transmission of financial data, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and customer service.
The integration of fiber optic cables into data communication systems marks a significant leap towards future-proofing global connectivity. As technology continues to evolve, the reliance on fiber optics is expected to grow, underscoring its importance in the digital age.
Are you ready to upgrade to the speed and reliability of fiber optic technology? Contact Gruber Communications today to discover how our fiber optic solutions can transform your organization’s connectivity and operational efficiency.
Efficient cable management is essential in today’s data centers, telecom rooms, and
Learn More →For many years, coaxial wire has been one of the most reliable
Learn More →